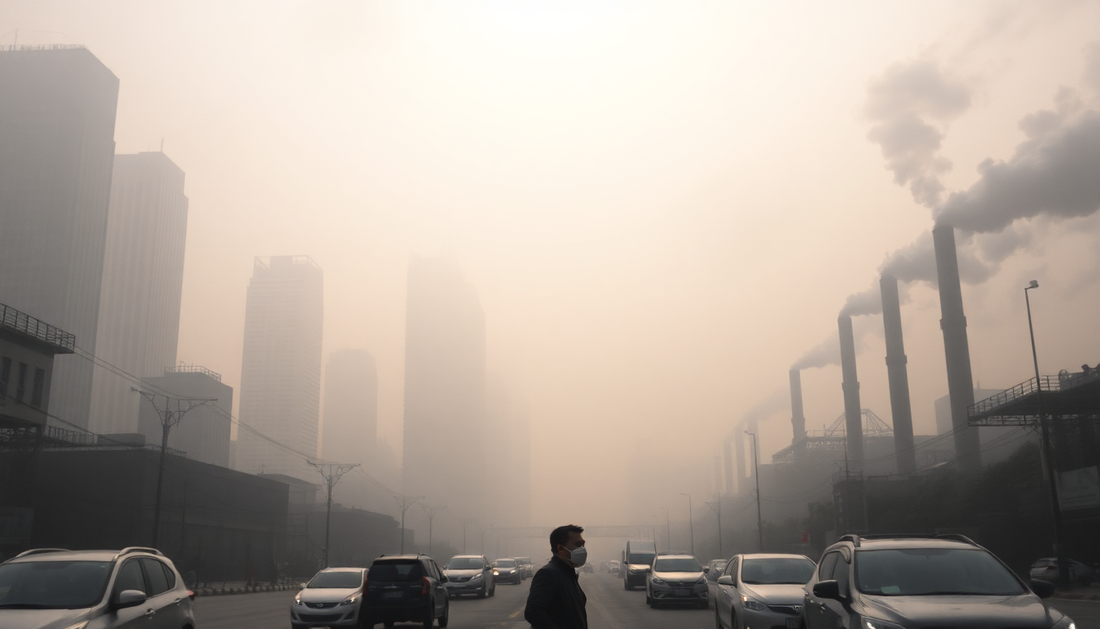
Air pollution is a global issue that affects us all, regardless of where we live. It is an invisible threat that can have far-reaching consequences on our health, the environment, and our way of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the complexities of air pollution, its sources, its impact, and the strategies being employed to combat this pressing challenge.
What is Air Pollution?
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air, including particulate matter, gases, and biological contaminants. These pollutants can originate from natural sources, such as volcanic eruptions and wildfires, as well as human-made sources, including industrial emissions, transportation, and agricultural practices.
The impact of air pollution is global in scale, with developed and developing countries alike grappling with its effects. From respiratory issues to climate change, the consequences of poor air quality are far-reaching and demand our collective attention.
Sources of Air Pollution
Air pollution can come from a variety of sources, both natural and human-made. Understanding these sources is crucial in developing effective strategies to mitigate the problem.
Natural Sources
- Volcanic eruptions: Volcanic activity can release large amounts of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants into the atmosphere.
- Wildfires: The burning of vegetation and other organic matter can release a wide range of pollutants, including particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds.
- Dust storms: Arid and semi-arid regions can experience dust storms that can transport large quantities of particulate matter over long distances.
Human-Made Sources
- Industrial Emissions
- Manufacturing processes: Factories and industrial facilities can release a variety of pollutants, including particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides.
- Power generation: The burning of fossil fuels for electricity production is a major source of air pollution, particularly in regions with a heavy reliance on coal-fired power plants.
- Transportation
- Vehicles: Exhaust emissions from cars, trucks, and other vehicles are a significant contributor to air pollution, releasing a mix of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide.
- Aviation: The combustion of jet fuel in aircraft engines can release a range of pollutants, including particulate matter and nitrogen oxides.
- Agricultural Practices
- Livestock farming: The decomposition of animal waste and the use of fertilizers can release methane, ammonia, and other pollutants.
- Crop burning: The practice of burning agricultural waste, such as crop residues, can release particulate matter and other pollutants into the air.
- Household Activities
- Heating and cooking: The burning of wood, coal, or other fuels for heating and cooking can release particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and other pollutants.
- Cleaning and personal care products: Certain household chemicals and products can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air.
Types of Air Pollutants
Air pollution can take many forms, and understanding the different types of pollutants is crucial in addressing the problem.
Particulate Matter (PM)
Particulate matter, or PM, refers to a complex mixture of solid and liquid particles suspended in the air. These particles can vary in size, with the smallest (PM2.5) being the most harmful to human health, as they can penetrate deep into the lungs.
Gaseous Pollutants
Gaseous pollutants include substances such as carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants can have a range of effects, from respiratory issues to the formation of ground-level ozone.
Biological Pollutants
Biological pollutants, such as mold, pollen, and bacteria, can also contribute to air pollution and have adverse effects on human health, particularly for those with allergies or respiratory conditions.
Health Effects of Air Pollution
The health consequences of air pollution are well-documented and can be severe, affecting both short-term and long-term well-being.
Respiratory Issues
Exposure to air pollutants can exacerbate respiratory conditions, such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer. Particulate matter and gaseous pollutants can irritate the lungs and airways, leading to coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Cardiovascular Problems
Air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and arrhythmias. The fine particles in the air can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition that narrows and hardens the arteries.
Neurological Impacts
Emerging research suggests that air pollution may also have adverse effects on the nervous system, potentially contributing to cognitive decline, Alzheimer's disease, and other neurological disorders.
Long-Term Health Consequences
Prolonged exposure to air pollution can have far-reaching health consequences, including reduced life expectancy, increased risk of chronic diseases, and impaired fetal development during pregnancy.
Environmental Impacts of Air Pollution
Air pollution not only affects human health but also has significant consequences for the environment.
Climate Change
Certain air pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and methane, are greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming and climate change. These changes can lead to more extreme weather events, sea level rise, and disruptions to ecosystems.
Acid Rain
Emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides can react with water in the atmosphere to form acid rain, which can damage vegetation, contaminate water bodies, and corrode buildings and infrastructure.
Ozone Depletion
Some air pollutants, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other halogenated compounds, can contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer, which protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Ecosystem Impacts
Air pollution can also have detrimental effects on ecosystems, including the loss of biodiversity, the disruption of food webs, and the degradation of habitats.
Measuring and Monitoring Air Pollution
Accurately measuring and monitoring air pollution is crucial for understanding the extent of the problem and developing effective solutions.
Air Quality Indices
Air quality indices (AQIs) are used to provide a standardized way of measuring and communicating air pollution levels. These indices typically take into account various pollutants and their concentrations, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of air quality.
Monitoring Technologies
Advances in technology have led to the development of sophisticated monitoring systems, including satellite-based remote sensing, ground-based sensor networks, and mobile monitoring platforms. These tools provide valuable data on air pollution levels and trends.
Global Air Quality Standards
Many countries and international organizations have established air quality standards and guidelines to help regulate and mitigate air pollution. These standards often vary based on local conditions and priorities, but they serve as a framework for improving air quality.
Air Pollution Control Strategies
Addressing the challenge of air pollution requires a multifaceted approach, involving a range of regulatory, technological, and behavioral strategies.
Regulatory Measures
Governments and policymakers play a crucial role in implementing laws and regulations to limit air pollution. These measures can include emission standards for industries, vehicle emissions regulations, and the promotion of clean energy sources.
Technological Solutions
Advancements in technology have led to the development of various solutions to reduce air pollution, such as:
- Emission control devices for vehicles and industrial facilities
- Renewable energy technologies to replace fossil fuels
- Energy-efficient building designs and appliances
- Air filtration and purification systems
Sustainable Practices
Individuals, communities, and businesses can also contribute to the fight against air pollution through the adoption of sustainable practices, such as:
- Reducing energy consumption and promoting energy efficiency
- Transitioning to cleaner modes of transportation, such as walking, cycling, or using public transit
- Minimizing the use of single-use plastics and promoting recycling
- Supporting local, sustainable agriculture and reducing food waste
Global Efforts to Combat Air Pollution
Addressing the global challenge of air pollution requires coordinated efforts at the international, national, and local levels.
International Agreements
Several international agreements and initiatives have been established to address air pollution, including the Paris Agreement on climate change, the Gothenburg Protocol on transboundary air pollution, and the United Nations Environment Programme's Clean Air Initiative.
National Policies
Many countries have implemented national policies and strategies to improve air quality, such as setting emission reduction targets, investing in clean energy, and promoting public awareness campaigns.
Non-Governmental Initiatives
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and community-based groups have also played a vital role in raising awareness, advocating for change, and implementing grassroots initiatives to combat air pollution.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
As we look to the future, there are both challenges and opportunities in the fight against air pollution.
Emerging Pollutants
As technology and industry evolve, new types of air pollutants may emerge, requiring ongoing research and the development of innovative solutions.
Innovative Solutions
Advancements in fields such as renewable energy, carbon capture and storage, and artificial intelligence offer promising opportunities to develop more effective and sustainable ways to address air pollution.
Public Awareness and Education
Fostering greater public awareness and education about the impacts of air pollution is crucial in driving individual and community-level action. Empowering citizens to make informed choices and participate in the solution-making process is key to long-term success.
Conclusion
Air pollution is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive, global response. By understanding the sources, types, and impacts of air pollution, as well as the strategies and efforts being employed to combat it, we can work towards a future with cleaner, healthier air for all. Through collective action, innovation, and a shared commitment to sustainability, we can overcome this invisible threat and create a more livable, resilient world for generations to come.