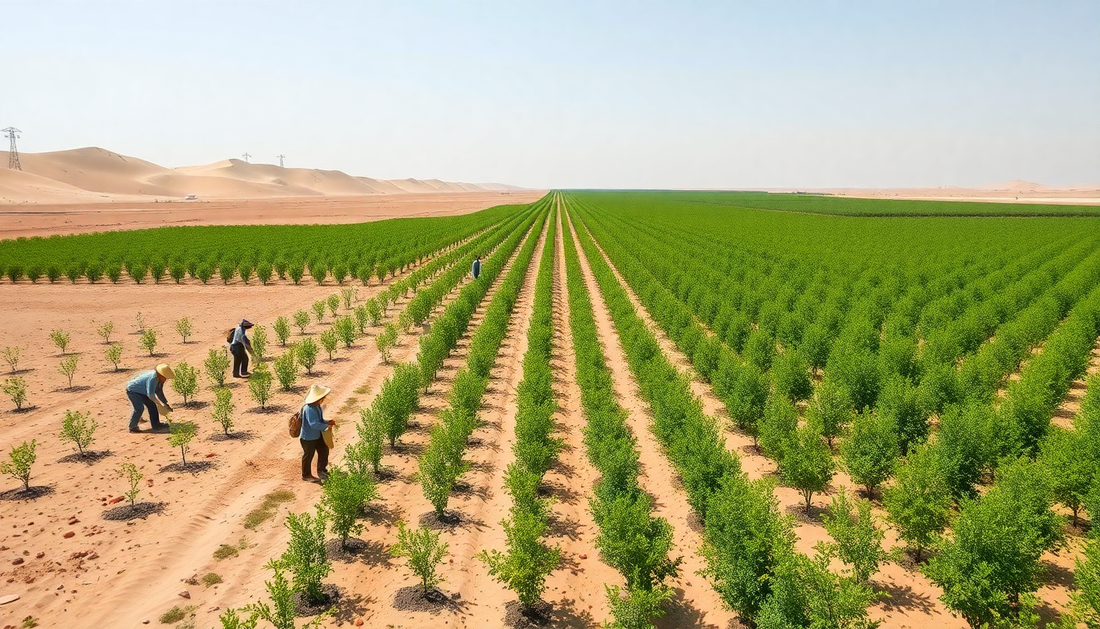
In the vast expanse of northern China, a remarkable initiative is underway – the construction of the Great Green Wall, an ambitious project aimed at combating the relentless march of desertification and restoring the region's fragile ecosystems. This colossal undertaking, spanning thousands of kilometers, is a testament to China's unwavering commitment to environmental preservation and the betterment of its people.
The Significance of the Great Green Wall
Desertification has long been a pressing issue in China, with the Gobi Desert and other arid regions steadily encroaching on arable land and threatening the livelihoods of millions. The Great Green Wall project, launched in the 1970s, represents a concerted effort to halt this alarming trend and reclaim the land for sustainable use. By establishing a vast network of trees, shrubs, and other vegetation, the initiative seeks to stabilize the soil, regulate the climate, and provide a buffer against the advancing desert.
Geographical Context and Historical Roots
The Great Green Wall project is primarily focused on the northern regions of China, where the Gobi Desert and other arid landscapes have been steadily expanding. This area, known as the "Three-North" region, encompasses the provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Gansu, Qinghai, and Xinjiang. The decision to launch the initiative was driven by a combination of environmental concerns and the need to address the socioeconomic challenges faced by communities in these regions.
Project Details and Strategies
The Great Green Wall project is a colossal undertaking, with the goal of establishing a continuous belt of vegetation stretching across more than 4,500 kilometers from the northeastern to the northwestern regions of China. The project involves the planting of a diverse array of tree species, including drought-resistant varieties such as pine, cedar, and oak, as well as shrubs and grasses that are well-suited to the local climate.
To ensure the success of the project, Chinese authorities have employed a range of innovative techniques and technologies. This includes the use of advanced irrigation systems, soil preparation methods, and even the deployment of drones to assist in the planting and monitoring of the vegetation. The project also involves the active participation of local communities, who are engaged in the planning, implementation, and maintenance of the green belt.
Environmental Impact and Benefits
The potential impact of the Great Green Wall project is truly staggering. By establishing a vast network of vegetation, the initiative aims to combat desertification, mitigate the effects of climate change, and restore the region's biodiversity. The trees and plants will help to stabilize the soil, reduce wind erosion, and improve water retention, ultimately leading to a more resilient and productive landscape.
Moreover, the project's environmental benefits extend far beyond the immediate region. By sequestering carbon and regulating the local climate, the Great Green Wall is expected to have a positive impact on global climate patterns, contributing to the broader efforts to address the challenges of climate change.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite the ambitious scope and noble intentions of the Great Green Wall project, it has not been without its challenges. The harsh environmental conditions of the northern regions, including extreme temperatures, limited rainfall, and poor soil quality, have posed significant obstacles to the successful establishment and maintenance of the vegetation. Additionally, the sheer scale of the project has presented logistical and financial hurdles, requiring a sustained commitment of resources and coordination among various stakeholders.
Progress and Achievements
Despite these challenges, the Great Green Wall project has made significant strides in recent years. According to official reports, more than 66 billion trees have been planted since the initiative's inception, with an estimated 85% survival rate. The project has also led to the restoration of over 7 million hectares of degraded land, providing tangible evidence of its environmental impact.
Moreover, the project has fostered a sense of community engagement and environmental stewardship among the local populations. Residents have been actively involved in the planting and maintenance of the vegetation, contributing to the long-term sustainability of the initiative.
Future Outlook and Global Implications
As the Great Green Wall project continues to evolve, its potential impact on a global scale cannot be overstated. The lessons learned and the successes achieved in China could serve as a model for other countries and regions facing similar environmental challenges. The project's emphasis on large-scale ecosystem restoration, community engagement, and the integration of innovative technologies could inspire similar initiatives around the world, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and resilient global environment.
Conclusion
The Great Green Wall project stands as a testament to China's unwavering commitment to environmental preservation and the betterment of its people. By combating desertification, restoring ecosystems, and fostering community engagement, this colossal undertaking represents a bold and visionary approach to addressing the pressing environmental challenges of our time. As the project continues to unfold, its impact will undoubtedly reverberate far beyond the borders of China, serving as a beacon of hope and inspiration for the global community.