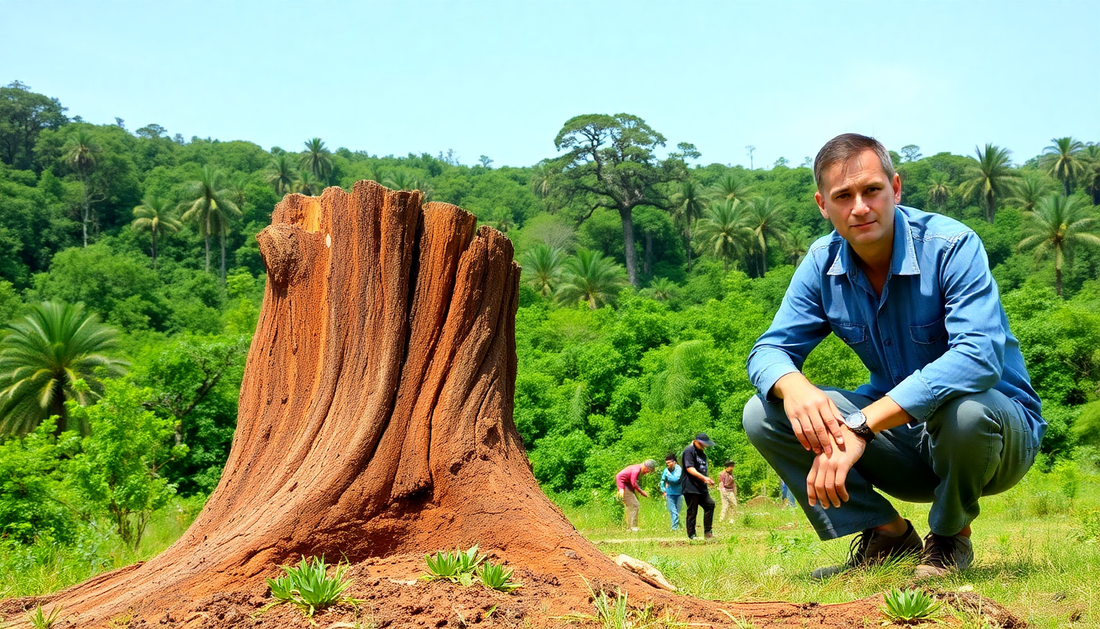
In a world where the demand for natural resources continues to grow, the fate of our forests has become a pressing global concern. Forests play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of our planet's ecosystems, providing essential habitats for countless species, regulating the climate, and sustaining the livelihoods of millions. Yet, the relentless pursuit of economic growth has led to the alarming depletion of these invaluable natural treasures.
The Importance of Forests
Forests are the lungs of our planet, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing life-giving oxygen. They are home to a staggering diversity of flora and fauna, many of which remain undiscovered. These verdant sanctuaries also play a crucial role in regulating the water cycle, preventing soil erosion, and mitigating the effects of natural disasters. Forests are not merely a resource to be exploited; they are the very foundation upon which our existence depends.
The Process of Wood Harvesting
Historically, the harvesting of wood has been a vital part of human civilization, providing the raw materials for construction, fuel, and a myriad of other essential products. Traditional logging methods, such as selective cutting and sustainable forestry practices, have long been employed to meet the demand for timber. However, the advent of modern machinery and the ever-increasing pressure to maximize profits have led to a shift towards more intensive and often unsustainable wood-harvesting techniques.
Traditional Logging Methods
In the past, logging operations were often carried out with a focus on preserving the long-term health of forests. Selective cutting, where only mature or diseased trees were removed, allowed for the regeneration of the forest ecosystem. This approach, combined with replanting efforts, helped to maintain the delicate balance of the forest.
Modern Forestry Techniques
Today, the landscape of wood harvesting has undergone a dramatic transformation. Large-scale clear-cutting, where entire swaths of forest are removed, has become a common practice, driven by the demand for rapid and efficient timber production. This approach, while maximizing short-term profits, has had devastating consequences on the environment.
Environmental Consequences of Excessive Wood Chopping
The relentless pursuit of wood resources has taken a heavy toll on the natural world, with far-reaching implications that extend beyond the immediate loss of forest cover.
Loss of Biodiversity
The destruction of forests has led to the displacement and extinction of countless species, many of which are yet to be discovered. The fragmentation of habitats and the loss of critical ecosystems have disrupted the delicate web of life, threatening the very foundation of our planet's biodiversity.
Soil Erosion and Degradation
The removal of trees and vegetation has left the soil vulnerable to erosion, leading to the depletion of vital nutrients and the degradation of once-fertile land. This, in turn, has had a cascading effect on agricultural productivity and the livelihoods of communities that rely on the land.
Climate Change Implications
Forests play a crucial role in regulating the global climate by absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide. The destruction of these natural carbon sinks has contributed significantly to the acceleration of climate change, with far-reaching consequences for the entire planet.
Disruption of Water Cycles
Forests are essential for maintaining the delicate balance of the water cycle, influencing precipitation patterns, groundwater recharge, and the overall availability of freshwater resources. The loss of forests has disrupted these vital processes, leading to water scarcity, flooding, and the degradation of aquatic ecosystems.
Economic and Social Impacts
The environmental consequences of excessive wood chopping have also had significant economic and social repercussions, particularly for the communities that rely on the forest for their livelihoods.
Effects on Local Communities
Indigenous and rural communities that have historically depended on the forest for their sustenance, cultural practices, and economic well-being have been disproportionately affected by the loss of these vital resources. The displacement of these communities and the disruption of their traditional ways of life have had profound social and economic consequences.
Global Economic Repercussions
The depletion of forest resources has had far-reaching economic implications, affecting industries that rely on timber and other forest-based products. Additionally, the environmental degradation caused by excessive wood chopping has led to increased costs associated with natural disaster mitigation, ecosystem restoration, and the development of alternative resources.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
In response to the growing concerns over the environmental impact of wood harvesting, there has been a renewed focus on the importance of sustainable forestry practices.
Responsible Forest Management
Sustainable forestry practices, such as selective cutting, replanting, and the preservation of old-growth forests, have been shown to maintain the long-term health and productivity of forest ecosystems. These approaches prioritize the balance between economic needs and environmental conservation.
Certification Programs
Certification programs, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI), have emerged as a way to ensure that wood and wood-based products are sourced from responsibly managed forests. These programs provide a framework for verifying the sustainability of forestry practices and promoting the use of eco-friendly products.
Alternatives to Wood Products
As the world grapples with the consequences of excessive wood chopping, the search for innovative and sustainable alternatives to wood-based products has become increasingly important.
Recycled Materials
The recycling and repurposing of existing wood products can help reduce the demand for new timber, thereby alleviating the pressure on forest resources. This approach not only conserves natural resources but also contributes to a more circular economy.
Eco-Friendly Substitutes
Advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of a wide range of eco-friendly alternatives to traditional wood-based products. These include materials made from agricultural waste, recycled plastics, and even mycelium-based composites, which offer similar properties to wood while minimizing environmental impact.
Government Policies and Regulations
Addressing the global challenge of deforestation and excessive wood chopping requires a comprehensive, multi-stakeholder approach, with governments playing a crucial role in shaping policies and regulations.
International Agreements
Global initiatives, such as the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement on climate change, have highlighted the importance of forest conservation and sustainable resource management. These international agreements have provided a framework for countries to collaborate and implement policies that protect forest ecosystems.
National Forest Protection Laws
Many countries have enacted legislation and regulations aimed at curbing deforestation and promoting sustainable forestry practices. These measures include restrictions on logging activities, the establishment of protected areas, and the implementation of reforestation programs.
The Role of Consumers
As individuals, we all have a responsibility to make informed choices that support the preservation of our forests and the transition towards a more sustainable future.
Making Informed Choices
By educating ourselves about the environmental impact of our purchasing decisions, we can actively choose products that are sourced from responsibly managed forests or made from eco-friendly alternatives. This collective action can drive the demand for sustainable products and incentivize businesses to adopt more environmentally-conscious practices.
Supporting Sustainable Products
Consumers can play a vital role in supporting the growth of the sustainable forestry and eco-friendly product industries. By choosing certified wood products, recycled materials, and innovative substitutes, we can contribute to the shift towards a more sustainable future.
Future Outlook
As we grapple with the urgent need to curb excessive wood chopping and protect our forests, there are glimmers of hope on the horizon. Emerging technologies and innovative approaches hold the promise of a more sustainable future.
Emerging Technologies in Forestry
Advancements in remote sensing, data analytics, and automation are transforming the way we manage and monitor forest resources. These technologies can help optimize forestry practices, detect illegal logging activities, and support reforestation efforts.
Reforestation Efforts
Around the world, governments, non-profit organizations, and community-based initiatives are working to restore degraded forests and plant new trees. These reforestation efforts not only replenish the lost forest cover but also contribute to the recovery of biodiversity and the mitigation of climate change.
Conclusion
The excessive chopping of our forests has had devastating consequences on the environment, the economy, and the social fabric of communities that depend on these vital resources. As we confront this global challenge, it is imperative that we take immediate and concerted action to preserve our forests and transition towards a more sustainable future.
By embracing responsible forestry practices, supporting eco-friendly alternatives, and making informed consumer choices, we can all play a role in safeguarding the health and resilience of our planet's forests. The time to act is now, for the sake of our present and the generations to come.