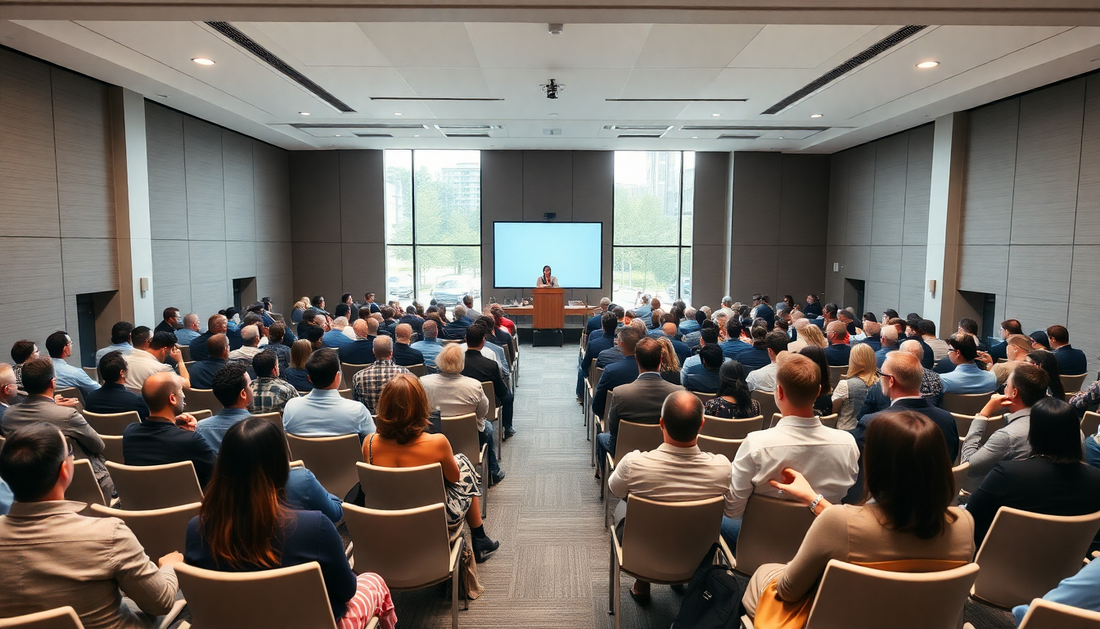
The 29th Conference of the Parties (COP29) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has concluded, marking a significant milestone in the global effort to address the pressing issue of climate change. As the world's leaders, policymakers, and stakeholders convened to chart the course for a sustainable future, the outcomes of this pivotal event have far-reaching implications for the planet and its inhabitants.
The Importance of Global Climate Agreements
Climate change is undoubtedly one of the most pressing challenges facing humanity today. The scientific consensus is clear: human-induced global warming is causing unprecedented changes in the Earth's climate, with devastating consequences for ecosystems, economies, and human well-being. Global cooperation and collective action are essential to mitigate the risks and adapt to the inevitable impacts of climate change.
The COP process, established by the UNFCCC, provides a crucial platform for nations to come together, negotiate, and forge agreements that guide global climate action. These agreements serve as the foundation for coordinated efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mobilize climate finance, and build resilience to the effects of climate change. The outcomes of COP29 are, therefore, of paramount importance in shaping the future of our planet.
Key Agreements at COP29
The COP29 negotiations resulted in several significant agreements and commitments that will shape the global climate landscape in the years to come. Among the key outcomes are:
Emission Reduction Targets
One of the primary objectives of COP29 was to secure stronger commitments from nations to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. After intense negotiations, the participating countries agreed to a collective target of limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement. This target will require unprecedented efforts by all nations to accelerate their emission reduction plans and implement ambitious policies.
Climate Finance Commitments
The issue of climate finance, particularly the provision of financial resources from developed to developing countries, has long been a contentious point in climate negotiations. At COP29, the participating nations reached a landmark agreement to establish a new, dedicated fund for loss and damage, providing much-needed support to vulnerable countries facing the devastating impacts of climate change. Additionally, commitments were made to significantly scale up climate finance flows to support mitigation and adaptation efforts in the Global South.
Adaptation and Resilience Measures
Recognizing the urgent need to address the growing impacts of climate change, COP29 placed a strong emphasis on adaptation and resilience-building measures. Agreements were reached to enhance support for developing countries in strengthening their capacity to adapt to the effects of climate change, including through the provision of technical assistance, technology transfer, and dedicated funding streams.
Specific Sectors Addressed
The COP29 negotiations also addressed specific sectors and areas that are critical to the global climate agenda. These include:
Energy Transition
The transition to clean, renewable energy sources was a central focus of the discussions, with commitments made to accelerate the phase-out of fossil fuels and scale up investments in solar, wind, and other low-carbon energy technologies. Specific targets and timelines were established to guide this energy transformation.
Transportation
The transportation sector, a major contributor to global emissions, was also a key area of attention. Agreements were reached to promote the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, improve public transportation systems, and support the development of sustainable aviation and shipping technologies.
Agriculture and Land Use
The role of agriculture and land-use practices in both contributing to and mitigating climate change was recognized. COP29 saw the establishment of frameworks to incentivize sustainable farming methods, protect and restore forests, and promote climate-smart agricultural practices.
Oceans and Biodiversity
Acknowledging the critical importance of healthy oceans and thriving ecosystems, COP29 included agreements to enhance ocean-based climate solutions, such as the protection and restoration of coastal habitats, as well as measures to safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Country-Specific Commitments
The COP29 negotiations also resulted in a range of country-specific commitments and pledges, reflecting the diverse national circumstances and priorities of the participating nations.
Major Emitters' Pledges
The world's largest emitters, including China, the United States, the European Union, and India, made significant commitments to accelerate their emission reduction efforts and align their national climate plans with the 1.5°C target.
Developing Nations' Contributions
Developing countries, often the most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, reaffirmed their commitment to climate action, while emphasizing the need for increased financial and technological support from the developed world.
Small Island States' Concerns
Small island developing states, facing existential threats from rising sea levels and other climate-related risks, successfully advocated for stronger adaptation measures and dedicated funding to address loss and damage.
Implementation Strategies
The success of the COP29 agreements will ultimately depend on the effective implementation of the commitments made by the participating nations. To this end, the negotiations also focused on developing robust implementation strategies, including:
Technology Transfer and Innovation
Agreements were reached to facilitate the transfer of clean technologies and promote innovation to support the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
Capacity Building Initiatives
Recognizing the need to strengthen the capabilities of developing countries, COP29 included commitments to invest in capacity-building programs and provide technical assistance.
Monitoring and Reporting Mechanisms
Robust monitoring, reporting, and verification systems were established to ensure transparency and accountability in the implementation of the COP29 agreements.
Challenges and Controversies
While the COP29 negotiations resulted in several landmark agreements, the process was not without its challenges and controversies. These include:
Disagreements among Parties
Tensions and diverging interests among the participating nations at times hindered the negotiation process, requiring complex compromises and trade-offs.
Gaps in Ambition and Action
Despite the progress made, many experts argue that the collective commitments from nations still fall short of what is required to achieve the 1.5°C target, highlighting the need for greater ambition and accelerated action.
Equity and Justice Concerns
Developing countries and marginalized communities continued to emphasize the importance of addressing the disproportionate impacts of climate change and ensuring a just transition to a sustainable future.
Global Reactions
The outcomes of COP29 have elicited a range of reactions from various stakeholders, including:
Environmental Organizations' Responses
Environmental advocacy groups and non-governmental organizations have praised the progress made at COP29 while calling for even bolder actions and greater accountability.
Business Sector Perspectives
The private sector has generally welcomed the COP29 agreements, recognizing the economic opportunities presented by the transition to a low-carbon economy, while also highlighting the need for supportive policies and incentives.
Public Opinion and Grassroots Movements
Grassroots climate movements and concerned citizens around the world have expressed both optimism and frustration, urging their governments to take more decisive action to address the climate crisis.
Future Implications
The outcomes of COP29 will have far-reaching implications for the global climate landscape in the years to come. These include:
Short-term Impacts on Policy and Industry
The COP29 agreements will immediately shape national climate policies, investment decisions, and the strategic planning of various industries, as they work to align their operations with the new global climate targets.
Long-term Projections for Climate Action
The commitments made at COP29 will be crucial in determining the trajectory of global climate action and the likelihood of achieving the Paris Agreement's long-term goals.
Preparations for COP30
The lessons learned and the unfinished agenda from COP29 will undoubtedly inform the preparations and expectations for the next Conference of the Parties, COP30, scheduled to take place in 2025.
Analysis and Expert Opinions
The COP29 agreements have been the subject of extensive analysis and commentary from a range of experts, including climate scientists, economists, and policymakers. Their assessments provide valuable insights into the potential impacts and challenges of the negotiated outcomes.
Scientific Community's Assessment
Climate scientists have generally welcomed the renewed commitments to limit global temperature rise, but have also emphasized the need for even more ambitious and immediate action to avert the most catastrophic consequences of climate change.
Economic Implications
Economists have highlighted the significant economic opportunities presented by the transition to a low-carbon economy, as well as the potential costs and disruptions that may arise from the implementation of the COP29 agreements.
Geopolitical Considerations
Geopolitical analysts have examined the COP29 negotiations through the lens of international relations, noting the complex dynamics and power dynamics that shaped the outcomes and their potential implications for global cooperation and security.
Conclusion
The 29th Conference of the Parties to the UNFCCC has undoubtedly marked a significant milestone in the global effort to address the climate crisis. The agreements reached at COP29, while not without their challenges and limitations, represent a crucial step forward in the collective journey towards a sustainable future.
As the world now turns its attention to the implementation of these commitments, the true test will be in the ability of nations, industries, and communities to translate the COP29 outcomes into tangible, measurable progress. The road ahead is undoubtedly long and arduous, but the stakes have never been higher. With renewed determination, global cooperation, and a steadfast commitment to climate action, the world can and must rise to the occasion, ensuring a livable planet for generations to come.