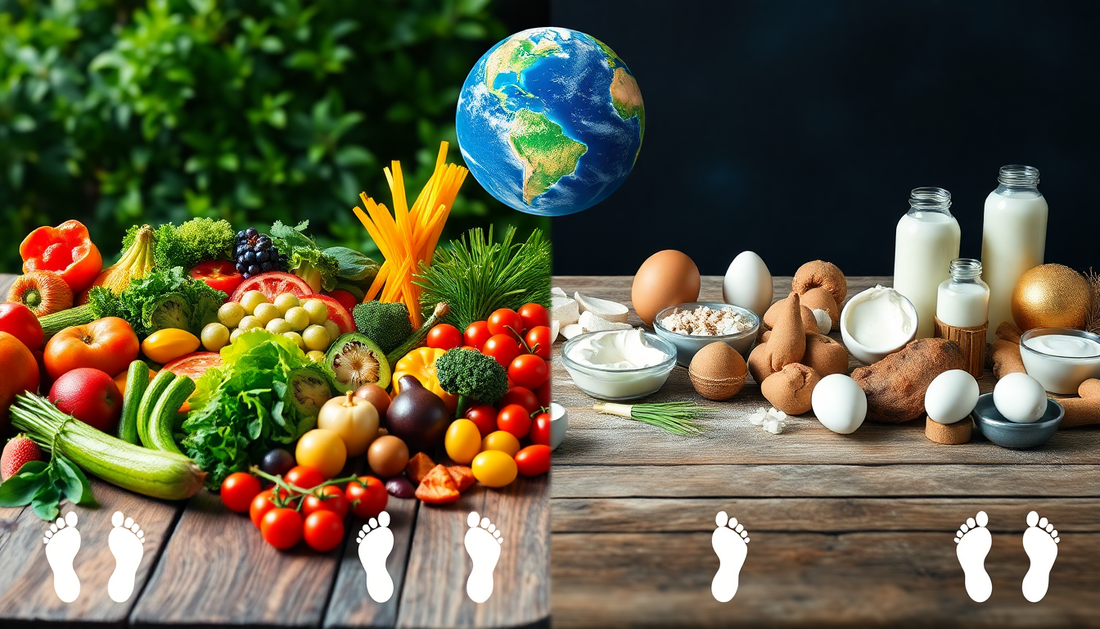
In recent years, the growing awareness of environmental sustainability has led many individuals to re-evaluate their dietary choices. As the world grapples with the pressing issues of climate change, resource depletion, and biodiversity loss, the question of whether a vegetarian or vegan diet is more eco-friendly has become a topic of increasing interest.
Defining Vegetarianism and Veganism
Vegetarianism is a dietary practice that excludes the consumption of meat, poultry, and seafood, but may include the consumption of dairy products and eggs. On the other hand, veganism is a more comprehensive lifestyle choice that eliminates the use of all animal-derived products, including not only meat, but also dairy, eggs, and even honey.
The key difference between these two dietary approaches lies in the level of animal product exclusion. While vegetarians avoid the consumption of animal flesh, they may still incorporate dairy and egg products into their diets. Vegans, on the other hand, completely abstain from using any animal-derived ingredients, making their diet and lifestyle more strictly aligned with the principles of animal welfare and environmental sustainability.
Environmental Impact of Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
When it comes to the environmental impact of these dietary choices, both vegetarian and vegan diets have been shown to have significant advantages over a traditional omnivorous diet.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The livestock industry is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for approximately 14.5% of the world's total. By eliminating or reducing the consumption of animal-based products, vegetarian and vegan diets can significantly lower an individual's carbon footprint. Studies have found that a vegan diet can reduce an individual's carbon emissions by up to 50% compared to a diet that includes meat and dairy.
Lower Water Consumption
Animal agriculture is also a highly water-intensive industry, with livestock production consuming a substantial amount of the world's freshwater resources. Vegetarian and vegan diets, which rely more heavily on plant-based foods, require significantly less water to produce the same amount of calories and nutrients. Estimates suggest that a vegan diet can reduce an individual's water footprint by as much as 50% compared to a diet that includes meat and dairy.
Decreased Land Use
The production of animal-based foods, particularly meat and dairy, requires a vast amount of land for grazing, feed cultivation, and other related activities. In contrast, plant-based diets generally have a much smaller land-use footprint, as they can produce more calories and nutrients per unit of land. This has important implications for preserving natural habitats and biodiversity.
Comparing Environmental Benefits: Vegetarian vs. Vegan
While both vegetarian and vegan diets offer significant environmental benefits, there are some key differences in their respective impacts.
Dairy and Egg Production
The production of dairy and egg products, which are still consumed by vegetarians, also has an environmental impact. The greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land requirements associated with dairy and egg production, although generally lower than those of meat production, can still contribute to the overall environmental footprint of a vegetarian diet.
Plant-based Alternatives
Vegan diets, which rely entirely on plant-based foods, can further reduce the environmental impact by eliminating the need for dairy and egg production. Additionally, the growing availability of plant-based alternatives, such as plant-based milks, cheeses, and meat substitutes, can provide nutritional and culinary options that are often more eco-friendly than their animal-derived counterparts.
Challenges and Considerations
While the environmental benefits of vegetarian and vegan diets are well-documented, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
Nutritional Concerns
Both vegetarian and vegan diets require careful planning to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients, such as protein, iron, and vitamin B12. Proper meal planning and the inclusion of a diverse range of plant-based foods can help address these nutritional concerns.
Sustainable Farming Practices
It's important to note that the environmental impact of any diet, including vegetarian and vegan diets, can be influenced by the farming practices used to produce the food. Sustainable and regenerative farming methods, such as organic agriculture and agroforestry, can further enhance the eco-friendliness of plant-based diets.
Food Processing and Packaging
The environmental impact of a diet can also be affected by the processing and packaging of the food. Minimally processed, locally sourced, and plant-based foods with eco-friendly packaging can help reduce the overall environmental footprint of a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Making the Transition: Tips for Adopting a More Eco-Friendly Diet
Transitioning to a more eco-friendly diet, whether it's vegetarian or vegan, can be a gradual process. Here are some tips to help you make the switch:
- Start with small, sustainable changes: Gradually reduce your consumption of animal-based products and explore plant-based alternatives.
- Experiment with new recipes and ingredients: Discover the wide variety of delicious and nutritious plant-based foods available.
- Prioritize local and seasonal produce: Reduce the environmental impact of your food by choosing locally grown, in-season fruits and vegetables.
- Educate yourself on plant-based protein sources: Incorporate a diverse range of plant-based proteins, such as legumes, nuts, and whole grains, to ensure a balanced diet.
- Seek support and resources: Connect with online communities, cookbooks, or local organizations to help you navigate the transition to a more eco-friendly diet.
Conclusion
In the face of pressing environmental challenges, the choice between a vegetarian or vegan diet can have a significant impact on an individual's environmental footprint. Both dietary approaches offer substantial benefits in terms of reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower water consumption, and decreased land use. While there are some nuances in their respective impacts, the overall conclusion is clear: adopting a more plant-based diet, whether vegetarian or vegan, is a powerful step towards a more sustainable future.
As we strive to create a greener and more eco-friendly world, making conscious food choices that align with our values and environmental concerns is a crucial part of the solution. By embracing a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle, we can not only improve our own health but also contribute to the preservation of our planet for generations to come.