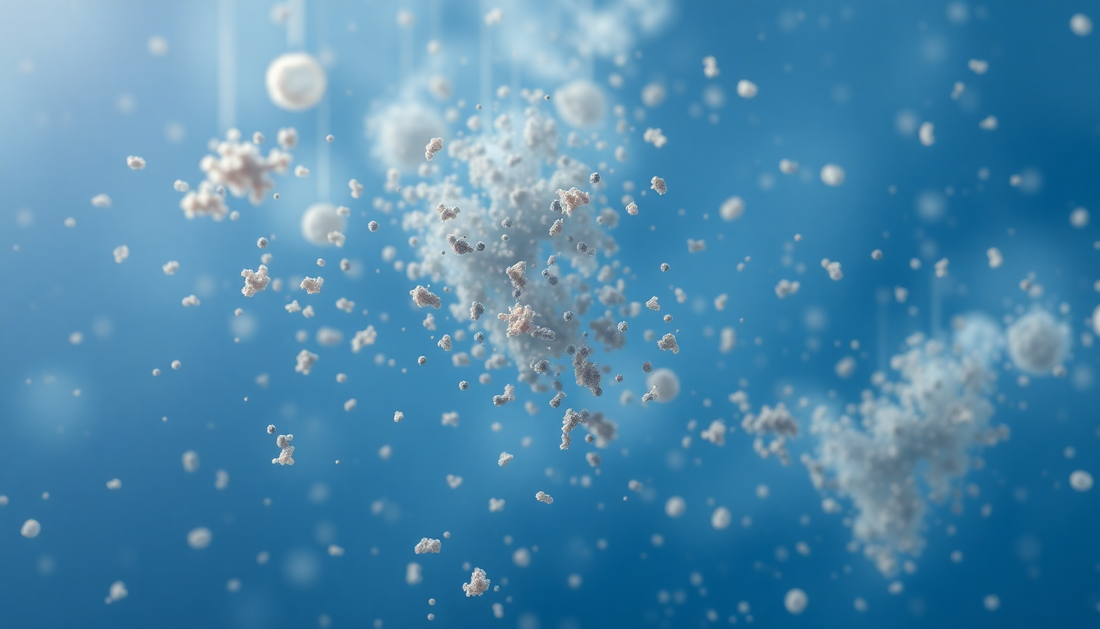
In the ever-evolving landscape of environmental challenges, one issue that has gained significant attention in recent years is the growing concern over particulate matter (PM) pollution. This invisible yet pervasive threat to our well-being has become a pressing global concern, with far-reaching implications for our health, the environment, and the quality of life we strive to maintain.
Introduction to Particulate Matter Pollution
Particulate matter, often referred to as PM, is a complex mixture of microscopic solid and liquid particles suspended in the air. These particles can vary in size, composition, and origin, and their impact on our health and the environment can be profound. At the forefront of this issue is the focus on PM2.5, a specific subset of particulate matter that has garnered significant attention due to its potential for causing serious health problems.
PM2.5, or fine particulate matter, refers to particles that are 2.5 micrometers or smaller in diameter. These tiny particles are small enough to be inhaled deep into the lungs, where they can cause a range of respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Understanding the nature of PM2.5 and its sources is crucial in addressing the growing concern over air pollution and its impact on our well-being.
Types of Particulate Matter
Particulate matter can be classified into different categories based on its size and composition. PM2.5, the primary focus of this discussion, is characterized by its small size and ability to penetrate deep into the respiratory system. These fine particles are typically generated by a variety of sources, including combustion processes, industrial activities, and even natural phenomena like wildfires and dust storms.
In addition to PM2.5, there is also a larger category of particulate matter known as PM10, which includes particles up to 10 micrometers in diameter. While these larger particles may not pose the same level of health risks as their smaller counterparts, they can still contribute to air pollution and have environmental consequences.
Health Impacts of PM2.5
The health implications of PM2.5 exposure are well-documented and a significant cause for concern. These tiny particles can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, triggering a range of adverse effects. Exposure to PM2.5 has been linked to an increased risk of respiratory diseases, such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer. Additionally, PM2.5 has been associated with cardiovascular problems, including heart attacks, strokes, and the exacerbation of existing heart conditions.
The long-term effects of PM2.5 exposure can be particularly devastating, as prolonged exposure has been shown to contribute to the development of chronic diseases and reduced life expectancy. Understanding the mechanisms by which PM2.5 affects our health is crucial in developing effective strategies to mitigate its impact and protect vulnerable populations.
Gaseous Matter Pollution
While particulate matter is a significant component of air pollution, it is not the only concern. Gaseous pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ozone (O3), also play a crucial role in the overall air quality and environmental health. These gaseous pollutants can interact with particulate matter, creating a complex and often synergistic relationship that can amplify the negative effects on human health and the environment.
The interplay between particulate matter and gaseous pollutants is a crucial aspect of understanding the broader implications of air pollution. By addressing both particulate and gaseous pollution, we can develop more comprehensive strategies to improve air quality and safeguard the well-being of our communities.
Measurement and Monitoring
Accurately measuring and monitoring air pollution levels is essential for understanding the scope of the problem and developing effective mitigation strategies. Air quality indices (AQIs) have been established to provide a standardized way of communicating the level of air pollution and its potential health impacts.
Advances in monitoring technologies, such as real-time sensors and satellite-based monitoring, have greatly improved our ability to track and analyze air pollution data on a global scale. This data is crucial for informing policymakers, guiding public health interventions, and empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their exposure to air pollutants.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Addressing the challenge of particulate matter pollution requires a multifaceted approach that involves both individual and collective efforts. On the personal level, adopting protective measures, such as the use of high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, can help reduce exposure to harmful particles. Additionally, promoting behavioral changes, such as reducing the use of fossil fuels and supporting the transition to cleaner energy sources, can contribute to the overall reduction of air pollution.
At the policy and regulatory level, governments and international organizations have a crucial role to play in implementing stringent air quality standards, promoting the development of clean technologies, and incentivizing the adoption of sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts between nations, industries, and civil society are essential in tackling this global issue and ensuring a healthier, more sustainable future for all.
Future of Air Quality Management
As we look to the future, the management of air quality and the mitigation of particulate matter pollution will continue to be a pressing challenge. Ongoing research and technological advancements are paving the way for innovative solutions that can help us better understand and address this complex problem.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced air filtration systems, smart city infrastructure, and real-time monitoring networks, hold the potential to revolutionize the way we monitor, manage, and mitigate air pollution. Additionally, global cooperation and the sharing of best practices will be crucial in ensuring that the lessons learned and the progress made in one region can be applied and adapted to benefit communities worldwide.
Conclusion
Particulate matter pollution, with its focus on the concerning issue of PM2.5, is a global challenge that demands our collective attention and action. By deepening our understanding of the nature, sources, and impacts of these tiny yet potent particles, we can develop more effective strategies to safeguard our health, the environment, and the quality of life we strive to maintain.
As individuals, we have a responsibility to make informed choices and adopt sustainable practices. And as a global community, we must work together to implement robust policies, support technological innovations, and foster a culture of environmental stewardship. Only through a comprehensive and collaborative approach can we truly address the pressing issue of particulate matter pollution and secure a healthier, more sustainable future for generations to come.