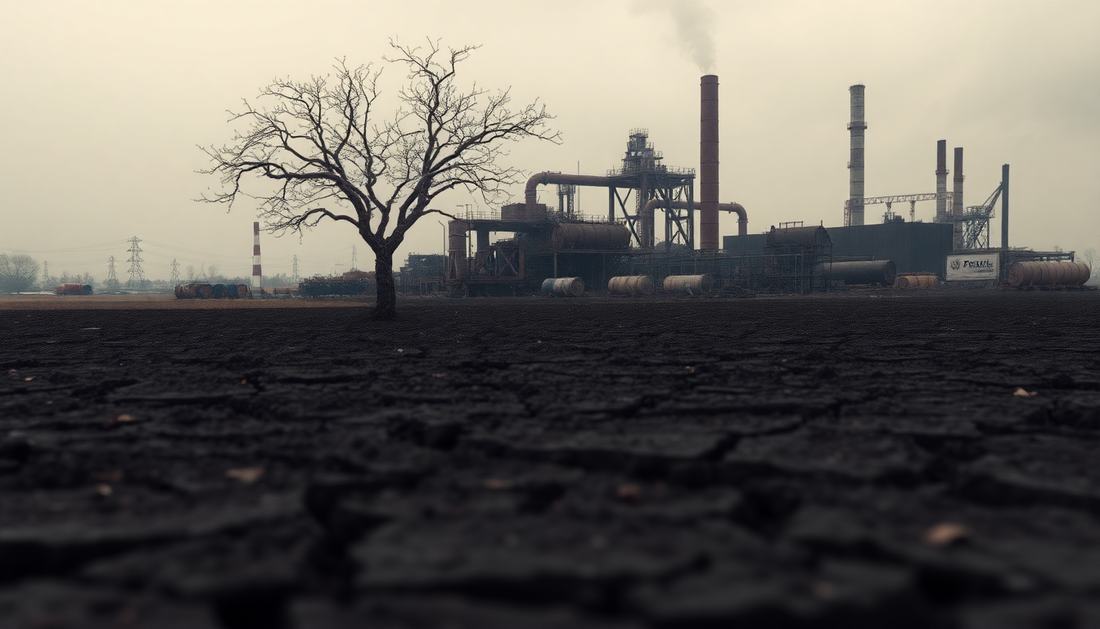
Land contamination is a pressing global issue that poses a significant threat to the health of our environment and the well-being of communities worldwide. As the world grapples with the consequences of industrialization, urbanization, and unsustainable agricultural practices, the contamination of our land has become a growing concern that requires immediate attention and concerted action.
Understanding Land Contamination
Land contamination refers to the presence of hazardous substances, such as chemicals, heavy metals, or radioactive materials, in the soil or groundwater. These contaminants can originate from a variety of sources, including industrial waste, chemical spills, mining activities, and the excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture. When these harmful substances seep into the land, they can have devastating effects on the surrounding ecosystem and the people who rely on it.
Major Sources of Land Contamination
One of the primary drivers of land contamination is the improper disposal of industrial waste. As manufacturing and production processes have become more complex, the volume of hazardous waste generated has increased exponentially. Without proper containment and treatment, these waste products often end up being dumped or buried, leading to the contamination of the soil and groundwater.
Another significant source of land contamination is the overuse of agricultural chemicals, such as pesticides and fertilizers. While these substances are designed to improve crop yields and protect plants from pests, their excessive application can lead to the accumulation of harmful residues in the soil, which can then be carried into nearby water sources or absorbed by the plants themselves.
Mining activities, too, have been a major contributor to land contamination. The extraction and processing of minerals often involve the use of toxic chemicals and the generation of large amounts of waste, which, if not properly managed, can seep into the surrounding environment and contaminate the land.
Environmental Consequences
The consequences of land contamination are far-reaching and can have devastating effects on the environment. Soil degradation is a common outcome, as the presence of harmful substances can disrupt the delicate balance of nutrients and microorganisms that are essential for healthy soil. This, in turn, can lead to a decline in agricultural productivity and the loss of valuable arable land.
Groundwater pollution is another major concern, as contaminants can leach into the water table and contaminate the sources of drinking water for both humans and wildlife. This can have serious implications for public health, as exposure to these pollutants can lead to a range of health problems, from respiratory issues to cancer.
The disruption of ecosystems is another significant consequence of land contamination. Toxic substances can accumulate in the food chain, leading to the decline of plant and animal populations and the disruption of the natural balance of the environment.
Case Studies: Lessons Learned
One of the most well-known cases of land contamination is the Love Canal incident in Niagara Falls, New York. In the 1970s, it was discovered that a former chemical waste disposal site had been covered over and turned into a residential neighborhood, exposing thousands of people to a cocktail of hazardous chemicals. The long-term effects of this contamination are still being felt today, with increased rates of birth defects, cancer, and other health issues among the affected community.
Another example is the Minamata disaster in Japan, where the release of mercury from a chemical plant led to the widespread contamination of the local environment and the poisoning of the local population. The effects of this disaster are still being felt decades later, with ongoing efforts to clean up the affected areas and provide support to the victims and their families.
Prevention and Remediation Strategies
Addressing the issue of land contamination requires a multi-pronged approach that involves both preventive measures and remediation strategies. On the preventive side, industries and agricultural producers must adopt more sustainable practices, such as the proper containment and treatment of waste, the responsible use of chemicals, and the implementation of cleaner production methods.
Governments, too, have a crucial role to play in this effort, by enacting and enforcing stricter regulations on land use, waste management, and environmental protection. Additionally, investment in research and development of innovative remediation technologies, such as soil washing, bioremediation, and phytoremediation, can help to address existing contamination and restore the health of the land.
At the community level, individuals can also contribute to the solution by supporting sustainable practices, advocating for stronger environmental policies, and participating in local cleanup and restoration efforts. By working together, we can tackle the challenge of land contamination and ensure a healthier, more resilient future for our planet.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Land contamination is a global crisis that demands our immediate attention and collective action. The consequences of this issue are far-reaching, affecting the health of our environment, the viability of our food systems, and the well-being of communities around the world. By addressing the root causes of land contamination and implementing comprehensive solutions, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for our planet.
The time to act is now. Let us come together as individuals, communities, and nations to prioritize the protection and restoration of our land, and to ensure that future generations inherit a world that is clean, healthy, and thriving.