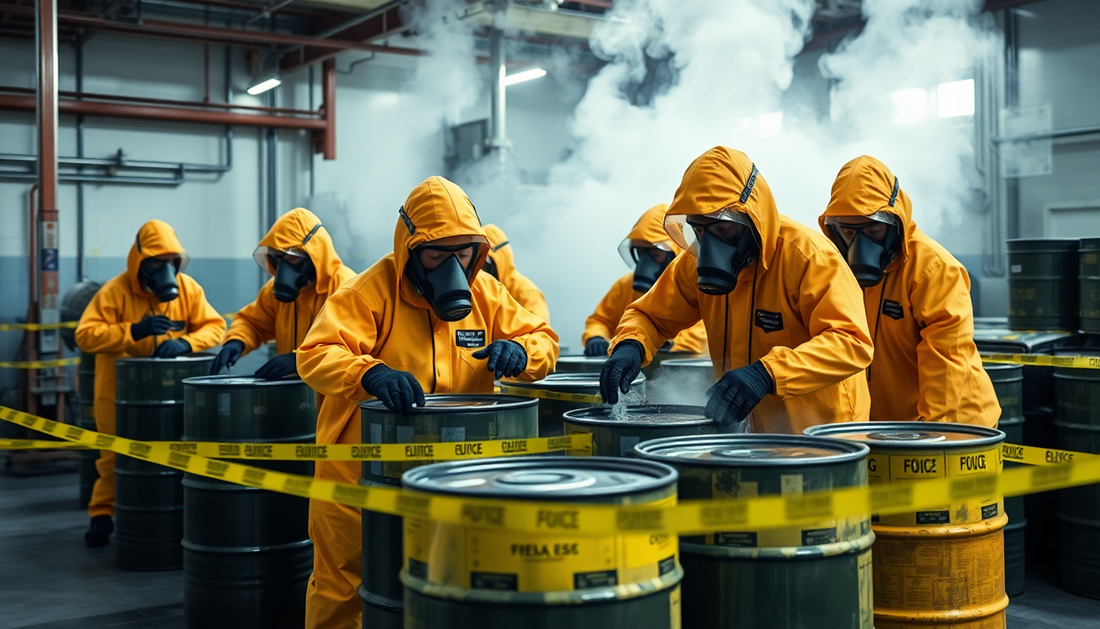
In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, the management of hazardous waste has become a critical concern for businesses across industries. As production processes become increasingly complex, the need to address the environmental impact and safety risks associated with hazardous materials has never been more pressing.
Understanding Hazardous Waste
Hazardous waste can take many forms, from toxic chemicals and heavy metals to flammable solvents and corrosive substances. These materials are often byproducts of various manufacturing operations, such as electroplating, painting, and chemical processing. Improper handling or disposal of these wastes can lead to serious consequences, including environmental contamination, worker exposure, and long-term ecological damage.
Risks and Environmental Impact
The risks associated with hazardous waste are multifaceted. Workers who come into direct contact with these materials face potential health hazards, ranging from respiratory issues to skin irritation and even long-term chronic conditions. Additionally, the release of hazardous substances into the environment can have far-reaching consequences, contaminating soil, water, and air, and disrupting delicate ecosystems.
Best Practices for Hazardous Waste Management
Effective hazardous waste management begins with proper identification and classification. Manufacturers must carefully assess the nature and composition of their waste streams, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards. This is followed by the implementation of safe handling protocols, which include the use of personal protective equipment, proper storage and containment methods, and the establishment of clear emergency response procedures.
Technological Solutions
Advancements in waste treatment and recycling technologies have opened up new avenues for sustainable manufacturing. From advanced thermal and chemical treatment processes to innovative recycling techniques, businesses can now explore a range of solutions to minimize their hazardous waste footprint. Additionally, the integration of monitoring and tracking systems can help manufacturers maintain a comprehensive understanding of their waste management practices, enabling continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the complex web of environmental regulations is a critical aspect of hazardous waste management. Manufacturers must stay informed about the latest legal requirements, which can vary significantly across different jurisdictions. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, legal consequences, and reputational damage, underscoring the importance of proactive and diligent waste management practices.
Case Studies
Numerous examples of successful hazardous waste reduction strategies can be found across various industries. In the automotive sector, for instance, some manufacturers have implemented closed-loop recycling systems, where waste materials are reintegrated into the production process, reducing the overall need for virgin resources. Similarly, in the electronics industry, companies have explored innovative ways to recover and repurpose valuable metals from discarded electronic components.
Conclusion
As the global push for sustainable manufacturing continues to gain momentum, the effective management of hazardous waste has become a critical imperative for businesses of all sizes. By embracing a comprehensive approach that combines best practices, technological advancements, and regulatory compliance, manufacturers can not only mitigate the environmental and safety risks associated with hazardous materials but also unlock new opportunities for cost savings, resource efficiency, and long-term competitive advantage. The path to a greener future starts with responsible waste management, and the time to act is now.